The cotton plant is native to tropical regions globally, most commonly in the Americas and Africa. Its cultivation and use date back thousands of years in Africa, playing a pivotal role in textile production, trade, and cultural practices. Globally, evidence of cotton textiles can be traced as far back as 6000 BC, and the plant was first introduced to Europe by Arab traders around 1 AD.
African civilizations such as ancient Egypt and the Mali Empire mastered cotton cultivation and weaving techniques, which became integral to their economies and societies. The production of cotton reached its zenith during the period of chattel slavery in the United States, when millions of Africans were forced into labor to cultivate cotton.


Cotton Plant Seed

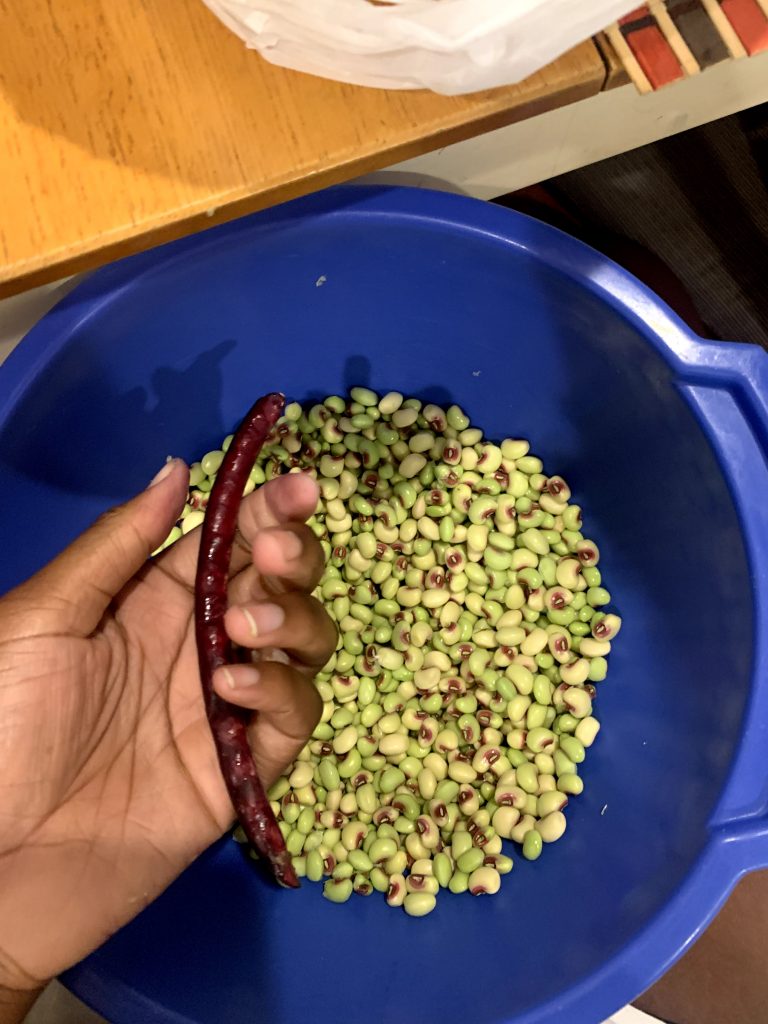
The black-eyed pea, also known as ‘cowpea’, is a versatile and nutritious legume with origins in West Africa. It is a small, creamy-white bean with a distinctive black spot, resembling an eye, hence its name. Black-eyed peas are a staple in many cuisines around the world, particularly in Africa, the Southern United States, and parts of Asia.
In the United States, black-eyed peas arrived with enslaved Africans among many other foods. For African ancestors, they provided supplemental nutrients including starches, protein, fiber and a variety of minerals and vitamins to their otherwise poor diet of fatback, molasses and grain flour.
Today, black-eyed peas are found in soul food dishes like Hoppin’ John. Cooked with fatback (or some other pork base), onions, and seasoning, the dish brings good luck into the new year. It is typically prepared alongside greens for money, cornbread for gold and pork for forward movement.

Black-eyed pea

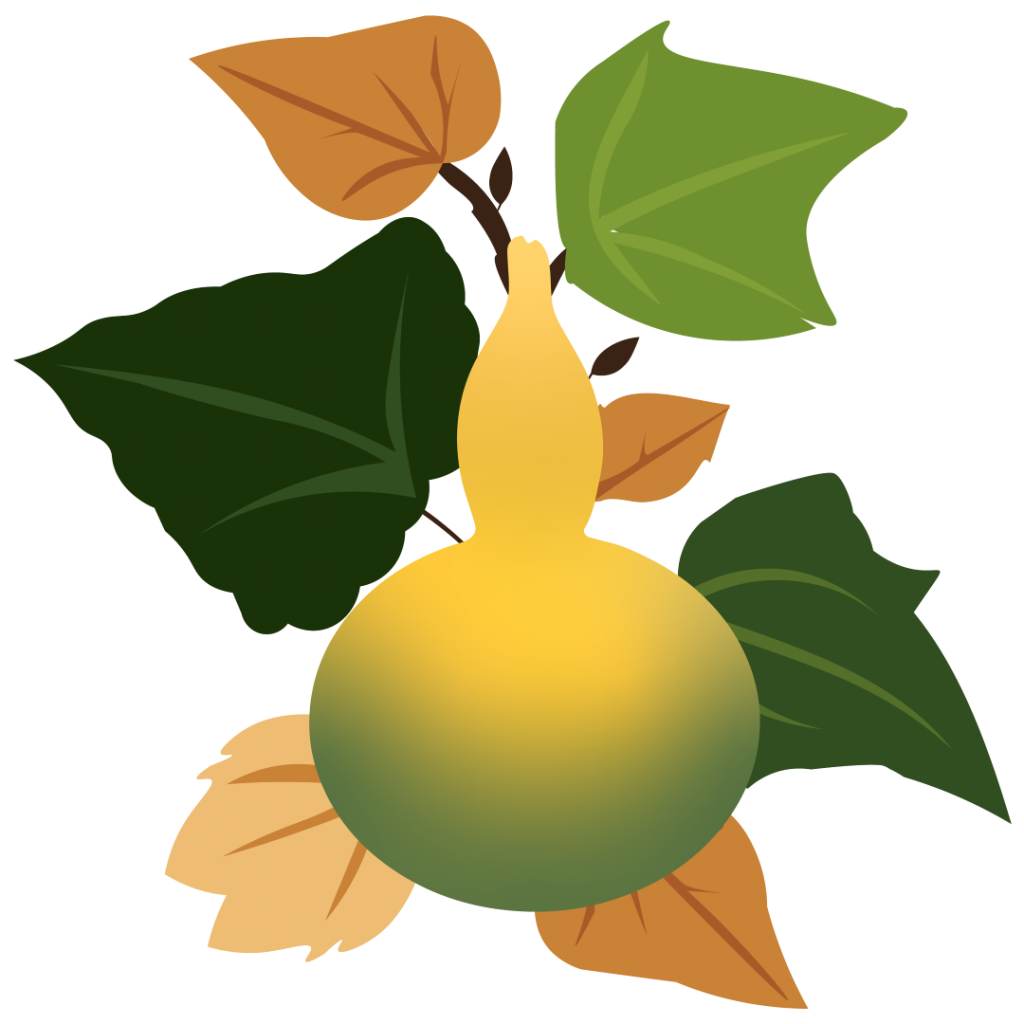
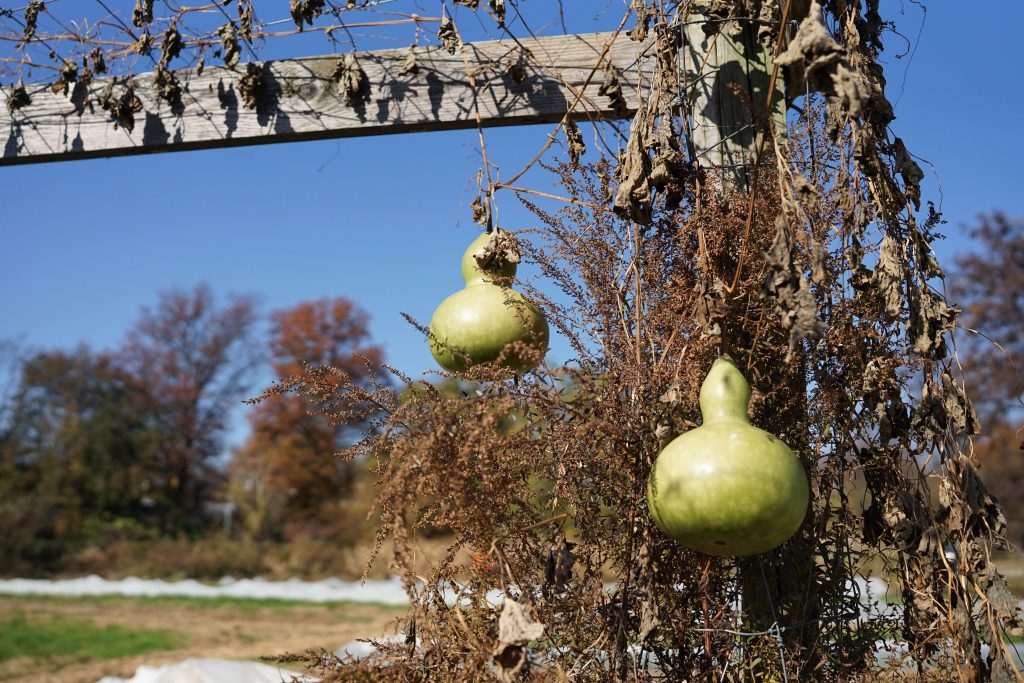
Bottle gourds, or calabash, are ancient melons, related to watermelons and cucumbers. First domesticated in East Africa and Asia, it may have spread across the globe via birds, humans, and even floating across the oceans long before European colonization of the Americas.
The bottle gourd is characterized by its elongated, bottle-like shape, which varies in size from small to large. It has a smooth, green, and sometimes mottled outer skin, while the flesh inside is pale green or white with soft seeds. The young, tender bottle gourd is often consumed as a vegetable, while the mature and dried gourd is used for various practical purposes. The bottle gourd is also used in Indian, Chinese, and Southeast Asian cooking.
The bottle gourd was among the crops that enslaved Africans in the Americas recognized from their native homelands in the Americas.



African rice grain
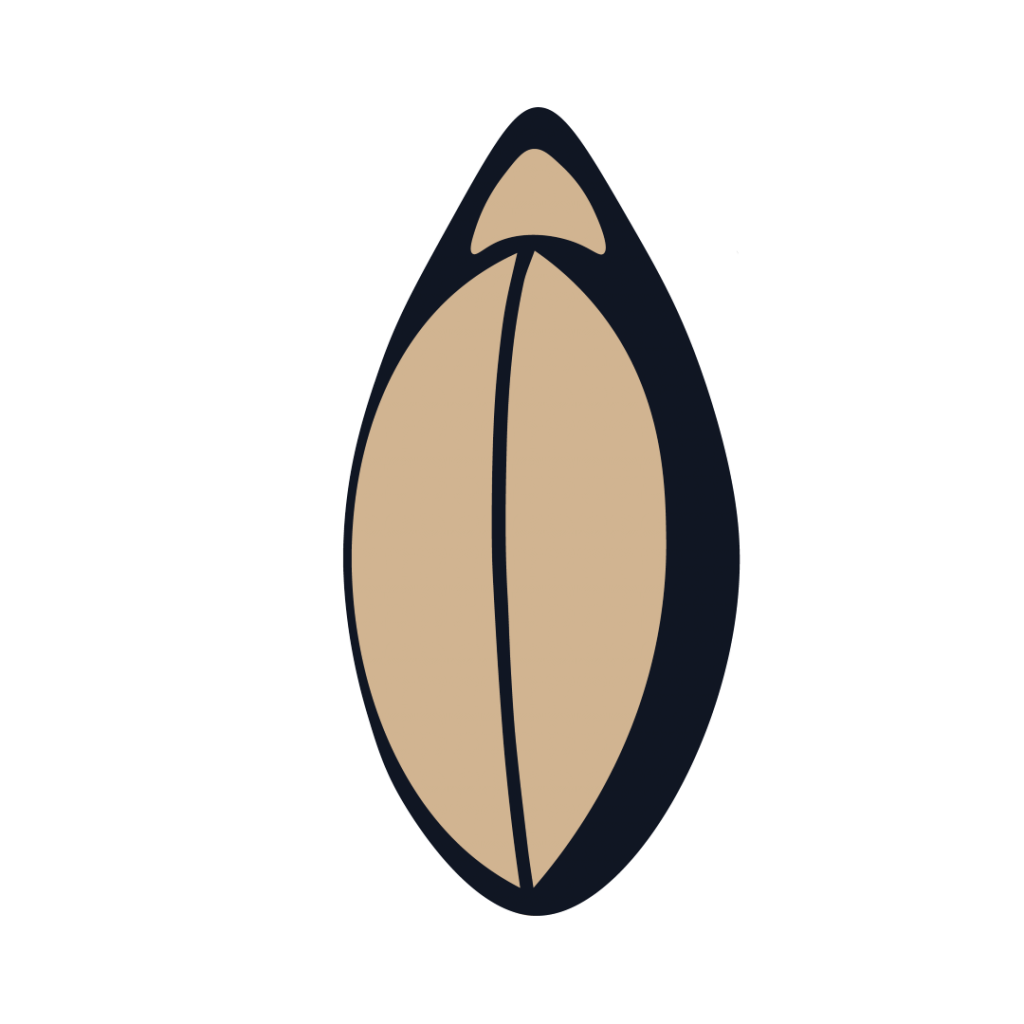
African rice is one of only two domesticated rice species. The other being Asian rice, which is more commonly sold today.
African rice was domesticated in West Africa in the Niger River basin and varities of African rice are pest-resistant, hardy, low-labor, and suited to dry, hot and tropical climate conditions. This variety of rice was brought to the Americas through the transatlantic slave trade as food on slave ships. It quickly became an established crop of the plantation economy earning the nickname “Carolina Gold” from the state that profitably produced it in the early days of the United States.
Rice plays a crucial role in global food security, providing a source of carbohydrates and nutrients for billions of people.